Multimodal RAG for PDFs with Text, Images, and Charts

Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (MM-RAG) systems are transforming the way you enhance Language Models and Generative AI. By incorporating a variety of data types within one application, these systems significantly expand their capabilities and applications.
While traditional RAG systems primarily use and parse text, Multimodal RAG systems integrate multimedia elements such as images, audio, and video. This integration is beneficial even for use cases that might initially seem like pure text scenarios, such as handling charts, data, and information stored as images.
By the end of this Multimodal RAG app template, you will:
- Learn what is Multimodal RAG: Gain a solid grasp of how these systems integrate multiple data types to enhance AI capabilities. Understand how these systems improve performance, especially with unstructured data and complex visual elements. This includes handling PDFs with images, charts, and tables stored as images.
- Run an App Template: See how to build and run a multimodal RAG application using open-source frameworks like Pathway. Specifically, we use GPT-4o to improve table data extraction accuracy, demonstrating superior performance over standard RAG toolkits. Implementing this approach allows your AI application to stay in sync with documents containing visually formatted elements.
If you want to skip the explanations, you can directly find the code here.
What is Multimodal RAG (MM-RAG)?
Multimodal Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) enhances LLM applications by incorporating text, images, audio, and video into the generation process. These systems retrieve relevant data from external sources and integrate it into the model’s prompt, enabling more accurate and contextually informed responses. This is particularly useful for understanding and generating content from diverse data formats. For example, in financial contexts, Multimodal RAG can efficiently interpret PDFs with complex tables, charts, and visualizations, significantly improving response accuracy.
How is Multimodal RAG Different from existing RAG?
Currently, most RAG applications are mostly limited to text-based data. This is changing with new generative AI models like GPT-4o, Gemini Pro, Claude-3.5 Sonnet, and open-source alternatives like LLaVA, which understand both text and images. Multimodal RAG systems leverage these models to give more coherent outputs, especially for complex queries requiring diverse information formats. This approach significantly enhances performance, as demonstrated in the example below.
Combining this with advanced RAG techniques like adaptive RAG, reranking, and hybrid indexing further improves MM-RAG reliability.

How is Multimodal RAG Different from Multimodal Search?
Multimodal search and Multimodal RAG (MM-RAG) both utilize deep learning models to create an embedding space—a map of meanings for texts, images, and audio. Similar items are placed close together, enabling efficient similarity searches across modalities like text and images. In multimodal search, you can find images based on text queries (text-to-image search) or text based on images (image-to-text search). This method maps data to a shared embedding space where items with similar meanings are grouped together. This is the basic principle behind how Google gives multimodal search results across images and texts.
However, unlike MM-RAG, which integrates retrieved data into the prompt for generating new content, multimodal search focuses on retrieving relevant results based on the query input. This makes multimodal search ideal for tasks like image or text searches in large datasets, while MM-RAG is better suited for generating responses that incorporate diverse data formats.
Key Benefits of Multimodal RAG
- Visual Data: Tables, charts, and diagrams, especially in critical use cases like financial documents, can be efficiently interpreted using models like GPT-4o. This enhances the accuracy of generative AI applications. An example of this can be seen in this guide, where visual data is parsed as images to improve understanding and searchability.
- Indexing: The explained content from tables is saved with the document chunk into the index, making it easily searchable and more useful for specific queries. This ensures that diverse data types are readily accessible, enhancing the system's performance and utility.
- Multimodal In-Context Learning: Modern multimodal RAG systems can perform in-context learning. This means they can learn new tasks from a small set of examples presented within the context (the prompt) at inference time. For instance, you can feed the model examples of images and text, and it will generate new images that follow the visual characteristics of the examples. This broadens the applications and effectiveness of multimodal RAG systems.
- Shared Benefits with Current RAG Systems: Privacy for enterprise use-cases, high accuracy, verifiability, lower compute costs, and scalability.
What's the main difference between LlamaIndex and Pathway?
Pathway offers an indexing solution that always provides the latest information to your LLM application: Pathway Vector Store preprocesses and indexes your data in real time, always giving up-to-date answers. LlamaIndex is a framework for writing LLM-enabled applications. Pathway and LlamaIndex are best used together. Pathway vector store is natively available in LlamaIndex.
Architecture Used for Multimodal RAG for Production Use Cases
Building a multimodal RAG system for production requires a robust and scalable architecture that can handle diverse data types and ensure seamless integration and retrieval of context. This architecture must efficiently manage data ingestion, processing, and querying, while providing accurate and timely responses to user queries. Key components include data parsers, vector databases, LLMs, and real-time data synchronization tools.
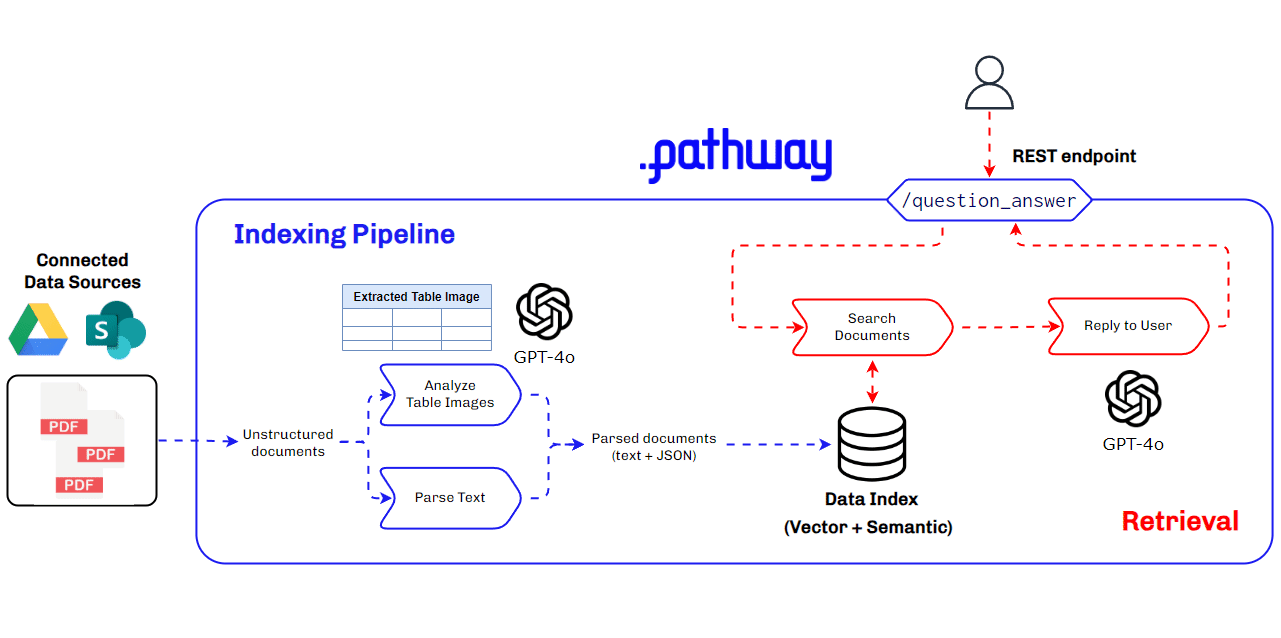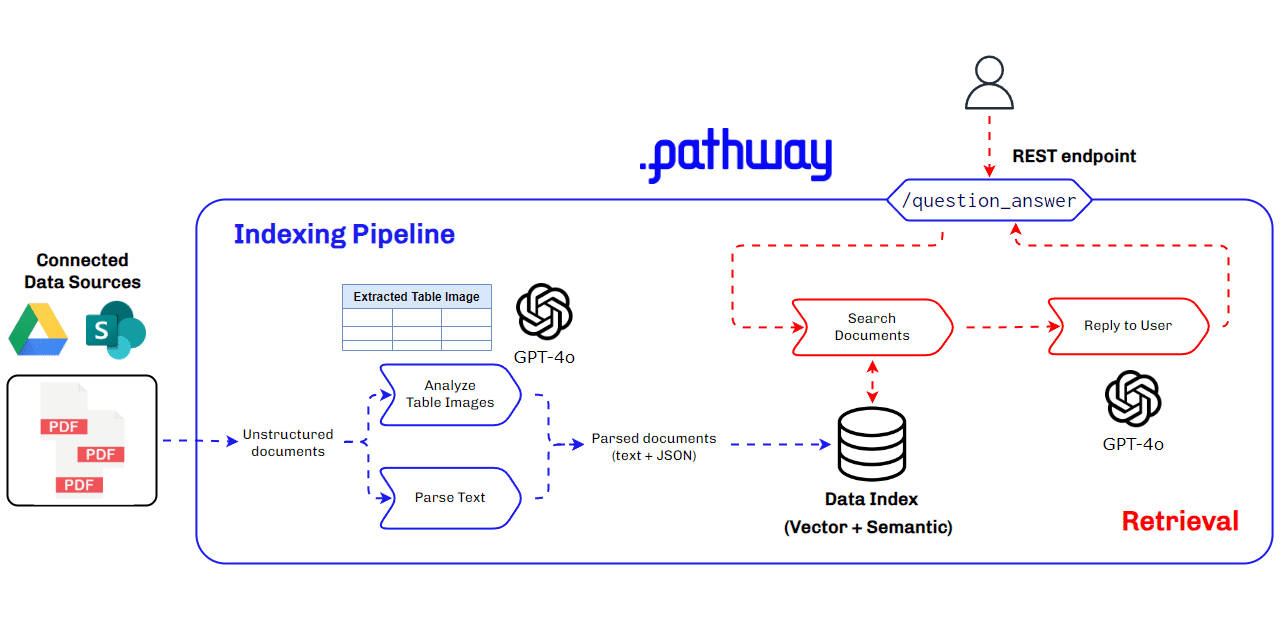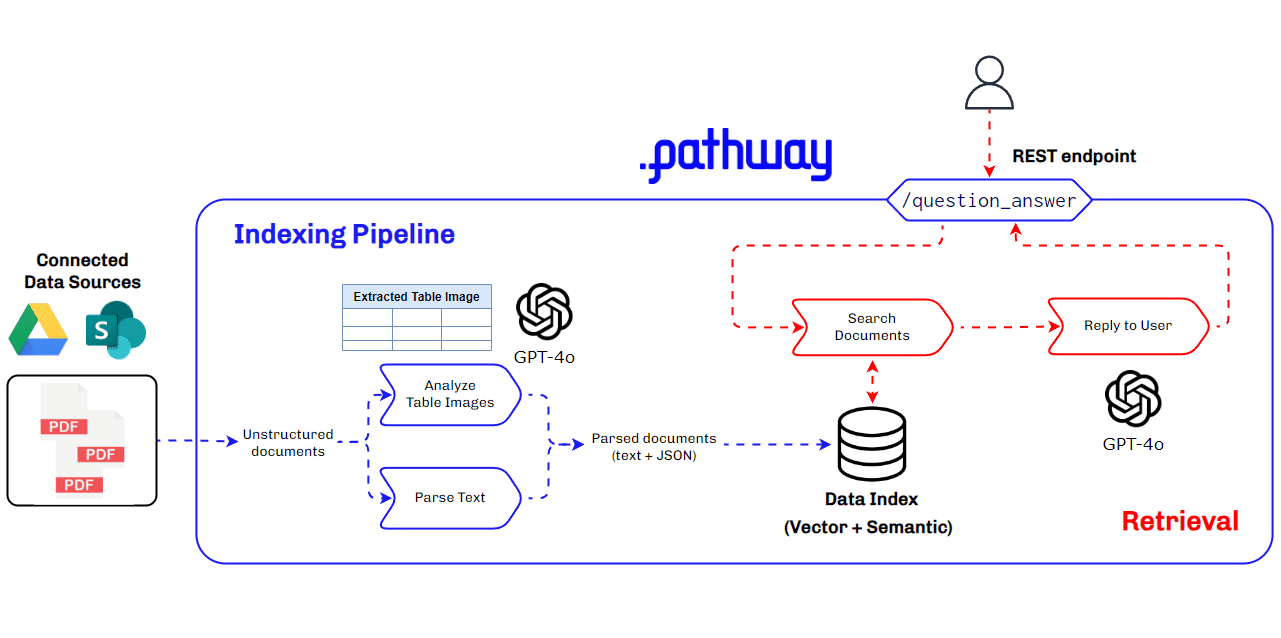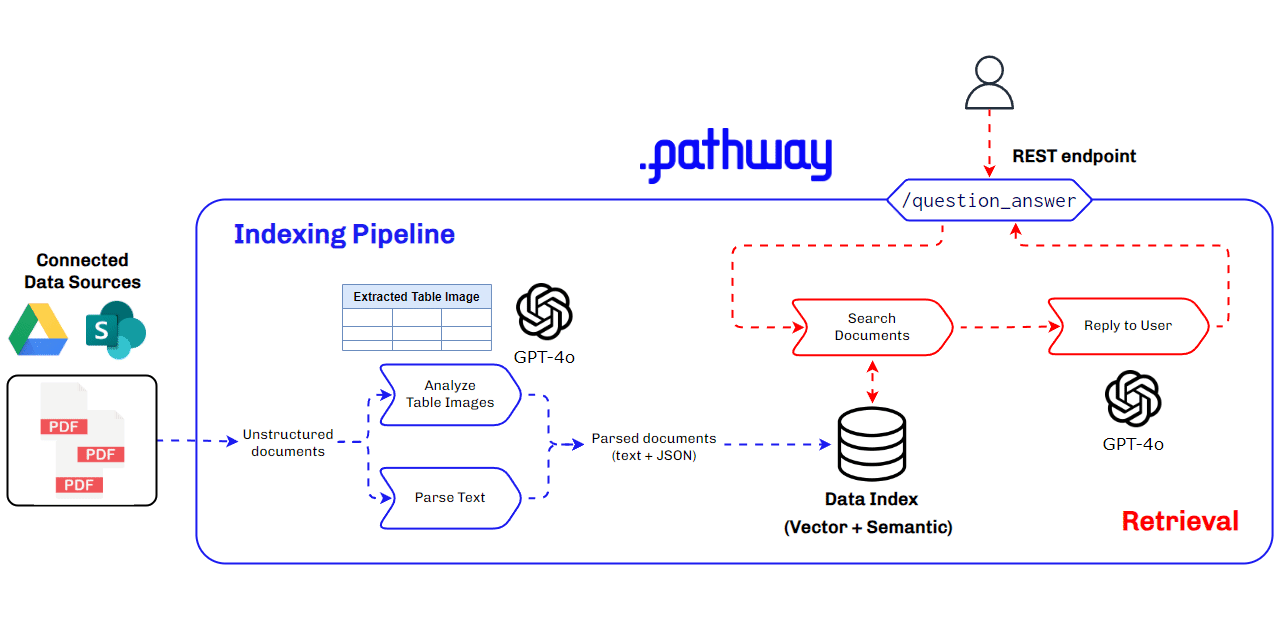
Key Components of the Multimodal RAG Architecture
- BaseRAGQuestionAnswerer Class: Integrates foundational RAG components.
- GPT-4o by Open AI: Used for extracting and understanding multimodal data, generating vector embeddings, and for answering queries with retrieved context.
- Pathway: Provides real-time synchronization, secure document handling, and a robust in-memory vector store for indexing.
This architecture ensures our multimodal RAG system is efficient, scalable, and capable of handling complex data types, making it ideal for production use cases, especially in finance where understanding data within PDFs is crucial.
Step by Step Guide for Multimodal RAG
In this guide, we focus on a popular finance use case: understanding data within PDFs. Financial documents often contain complex tables and charts that require precise interpretation.
Here we use Open AI’s popular Multimodal LLM, GPT-4o. It’s used at two key stages:
- Parsing Process: Tables are extracted as images, and GPT-4o then explains the content of these tables in detail. The explained content is saved with the document chunk into the index for easy searchability.
- Answering Questions: Questions are sent to the LLM with the relevant context, including parsed tables. This allows the generation of accurate responses based on the comprehensive multimodal context.
Install Pathway
Install Pathway and all its optional packages.
!pip install 'pathway[all]>=0.20.0'
Set Up OpenAI API Key
Set the OpenAI API key as an environment variable. Replace the placeholder with your actual API key.
OPENAI_API_KEY = "Paste Your OpenAI API Key here"
import os
# Set the OpenAI API key
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = OPENAI_API_KEY
Imports and Environment Setup
This cell sets up necessary imports and environment variables for using Pathway and related functionalities.
Key Imports:
- pathway: Main library for document processing and question answering.
Modules:
- udfs.DiskCache, udfs.ExponentialBackoffRetryStrategy: Modules for caching and retry strategies.
- xpacks.llm: Various tools for leveraging Large Language Models effectively.
- llm.parsers.DoclingParser: The
DoclingParserclass efficiently handles document parsing tasks, including text extraction and table parsing, providing a streamlined approach for document analysis and content extraction. - llm.question_answering.BaseRAGQuestionAnswerer: Sets up a base model for question answering using RAG.
- llm.vector_store.VectorStoreServer: Handles document vector storage and retrieval.
import pathway as pw
from pathway.udfs import DefaultCache, ExponentialBackoffRetryStrategy
from pathway.xpacks.llm import embedders, llms, parsers, prompts, splitters
from pathway.xpacks.llm.question_answering import BaseRAGQuestionAnswerer
from pathway.xpacks.llm.document_store import DocumentStore
Document Processing and Question Answering Setup
Create Data Directory
Create a data directory if it doesn't already exist. This is where the uploaded files will be stored. Then upload your pdf document.
You can also omit this cell if you are running locally on your system. Create a data folder in the current directory and copy the files. In that case please comment out this cell as this is for colab only.
Create the data folder if it doesn't exist
!mkdir -p data
# default file you can use to test
# to use your own data via the Colab UI, click on the 'Files' tab in the left sidebar, go to data folder (that was created prior to this) then drag and drop your files there.
!wget -q -P ./data/ https://github.com/pathwaycom/llm-app/raw/main/examples/pipelines/gpt_4o_multimodal_rag/data/20230203_alphabet_10K.pdf
Read Documents
Read the documents from the data folder. This cell assumes that the uploaded files are in the data folder.
folder = pw.io.fs.read(
path="./data/",
format="binary",
with_metadata=True,
)
sources = [
folder,
] # define the inputs (local folders & files, google drive, sharepoint, ...)
chat = llms.OpenAIChat(
model="gpt-4o",
retry_strategy=ExponentialBackoffRetryStrategy(max_retries=6),
cache_strategy=DefaultCache(),
temperature=0.0,
)
Configure and Run Question Answering Server
Configure and run the question answering server using BaseRAGQuestionAnswerer. This server listens on port 8000 and processes incoming queries.
app_host = "0.0.0.0"
app_port = 8000
parser = parsers.DoclingParser(
table_parsing_strategy="llm",
image_parsing_strategy="llm",
multimodal_llm=chat
)
splitter = splitters.TokenCountSplitter()
embedder = embedders.OpenAIEmbedder(cache_strategy=DefaultCache())
index = pw.indexing.BruteForceKnnFactory(embedder=embedder)
doc_store = DocumentStore(
sources,
retriever_factory=index,
splitter=splitter,
parser=parser,
)
app = BaseRAGQuestionAnswerer(
llm=chat,
indexer=doc_store,
search_topk=6,
)
app.build_server(host=app_host, port=app_port)
# app.run_server(with_cache=True, terminate_on_error=False)
import threading
t = threading.Thread(target=app.run_server, name="BaseRAGQuestionAnswerer")
t.daemon = True
thr = t.start()
List Documents
!curl -X 'POST' 'http://0.0.0.0:8000/v2/list_documents' -H 'accept: */*' -H 'Content-Type: application/json'
Ask Questions and Get Answers
Query the server to get answers from the documents. This cell sends a prompt to the server and receives the response.
Make changes to the prompt and ask questions to get information from your documents
!curl -X 'POST' 'http://0.0.0.0:8000/v2/answer' -H 'accept: */*' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{"prompt": "How much was Operating lease cost in 2021?"}'
Conclusion
This is how you can easily implement a Multimodal RAG Pipeline using GPT-4o and Pathway. You used the BaseRAGQuestionAnswerer class from pathway.xpacks, which integrates the foundational components for our RAG application, including data ingestion, LLM integration, database creation and querying, and serving the application on an endpoint. For more advanced RAG options, you can explore rerankers and the adaptive RAG example. For implementing this example using open source LLMs, here’s a private RAG app template that you can use as a starting point. It will help you run the entire application locally making it ideal for use-cases with sensitive data and explainable AI needs. You can do this within Docker as well by following the steps in Pathway’s LLM App templates repository.
To explore more app templates and advanced use cases, visit Pathway App Templates or Pathway’s official blog.